What is Osteopathy?
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What Does an Osteopath Do? 2.1 The Holistic Approach
- Conditions Osteopathy Can Help With
- How Osteopaths Treat the Body 4.1 Types of Techniques Used
- What to Expect During a Consultation 5.1 The Initial Assessment 5.2 Hands-On Treatment 5.3 Ongoing Management
- Is Osteopathy Evidence-Based?
- Conclusion
- FAQs About Osteopathy 7.1 What qualifications do osteopaths have in Australia? 7.2 How is osteopathy different from physiotherapy or chiropractic? 7.3 Do I need a referral to see an osteopath? 7.4 Is osteopathy covered by private health insurance?
- Author
Introduction
Osteopathy is a form of manual healthcare that focuses on the whole person, not just the symptoms. Founded in the late 1800s by Dr. Andrew Taylor Still, osteopathy has grown into a globally recognised allied health profession. In Australia, it is a regulated and evidence-based practice that uses a hands-on approach to support the body’s structure and function.
People often seek osteopathic care for musculoskeletal pain, such as back or neck discomfort, but its applications go much further. This blog will explore what osteopathy really is, how it works, what it treats, and what to expect when visiting an osteopath.
What Does an Osteopath Do?
Osteopaths are university-trained health professionals who use a range of techniques to assess, diagnose, treat and prevent conditions of the body.
2.1 The Holistic Approach
Osteopaths consider how the skeleton, joints, muscles, nerves, circulation, connective tissue and internal organs function as a whole. Their approach is based on the idea that the body has the innate ability to heal itself when functioning optimally. Rather than just treating symptoms, osteopaths look for the root cause of dysfunction.
- Detailed case history and physical examination
- Hands-on treatment techniques
- Education and advice for self-care
- Exercise prescription
- Referral to other professionals if necessary
Conditions Osteopathy Can Help With
Many people are surprised to learn the breadth of conditions osteopathy can assist with. Common presentations include:
- Lower back pain and sciatica
- Neck pain and headaches
- Postural issues and workplace strains
- Sporting injuries and tendon complaints
- Pregnancy-related discomfort
- Jaw pain and TMJ dysfunction
Osteopathy is suitable for people of all ages, from infants to the elderly, and is tailored to the individual’s needs.
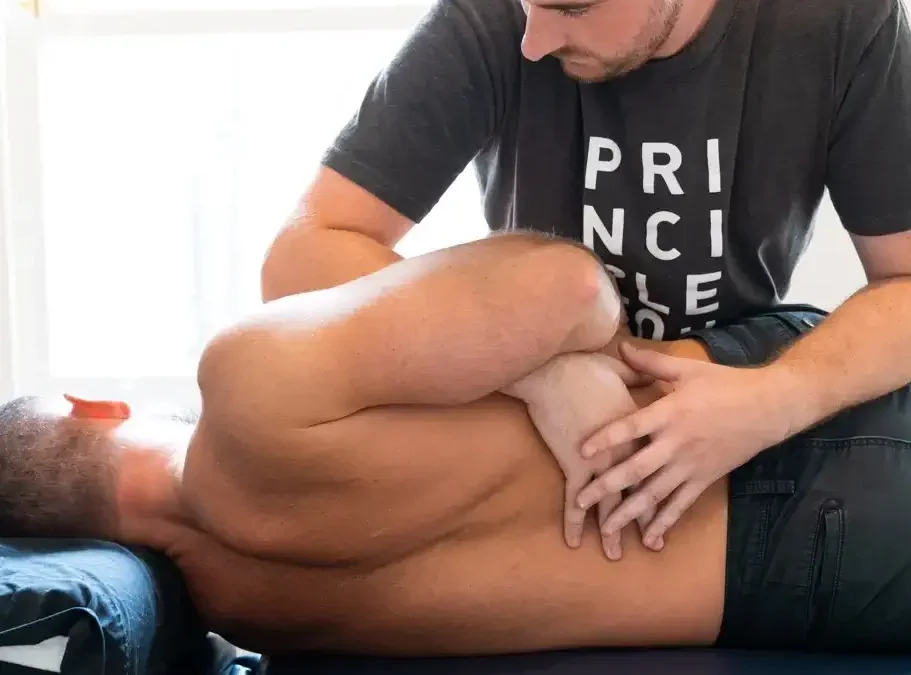
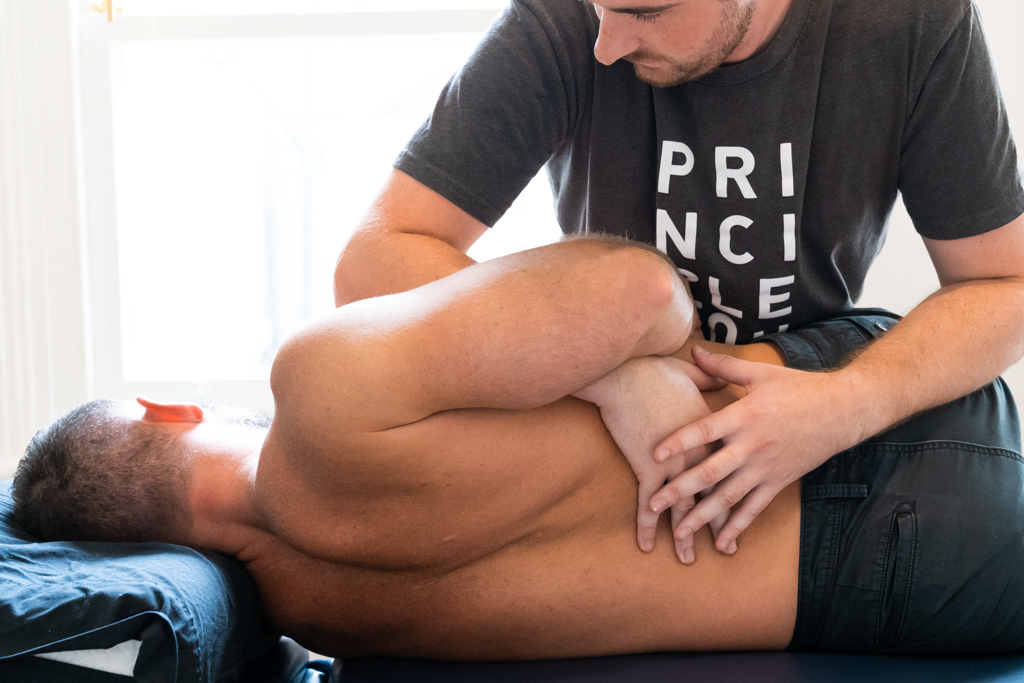
How Osteopaths Treat the Body
Treatment is hands-on and may include a wide range of manual therapy techniques, depending on the patient’s age, condition and preference.
4.1 Types of Techniques Used
- Soft tissue massage
- Joint articulation and mobilisation
- Spinal manipulation (when appropriate)
- Stretching techniques
- Gentle techniques for children and the elderly
These techniques aim to improve mobility, reduce pain and support the body’s own healing mechanisms.
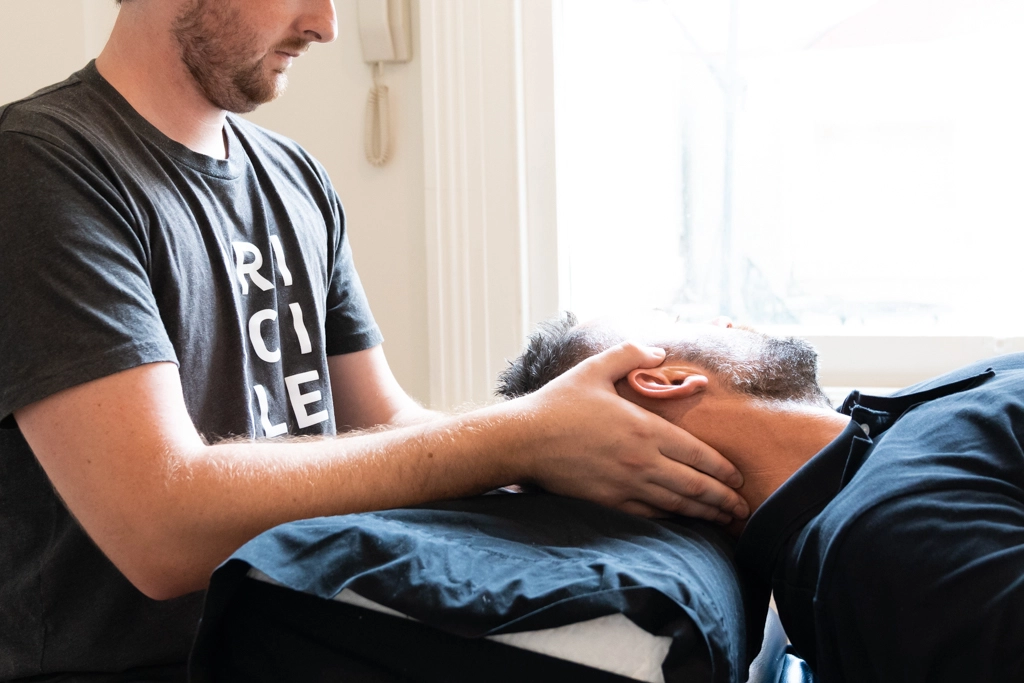
What to Expect During a Consultation
Visiting an osteopath for the first time can feel unfamiliar, but the process is professional and patient-focused.
5.1 The Initial Assessment
Your osteopath will ask detailed questions about your symptoms, medical history, lifestyle and goals. They will also assess your posture, movement, and perform specific clinical tests.
5.2 Hands-On Treatment
If appropriate, treatment is provided during your first visit. Techniques are chosen based on what is most suitable and safe for you.
5.3 Ongoing Management
You may be given advice on posture, activity modification, stretching or strengthening exercises. Your osteopath might also suggest follow-up sessions to support longer-term recovery or prevention.
Is Osteopathy Evidence-Based?
Yes. Osteopathy in Australia is a nationally regulated profession under the Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (AHPRA). Osteopaths must meet rigorous education and professional standards.
Research supports the effectiveness of osteopathic treatment for musculoskeletal pain, particularly lower back and neck pain, as well as improving function and reducing the need for medication. Osteopathy Australia provides ongoing research updates and professional education to ensure best practices are followed.
Key sources:
- Osteopathy Australia: https://www.osteopathy.org.au
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE)
- Australian Government Department of Health
Conclusion
Osteopathy offers a safe, effective and patient-centred approach to healthcare. It blends manual therapy, movement education, and holistic assessment to help individuals recover from injury and maintain good physical function.
Whether you’re dealing with a new injury, ongoing discomfort, or simply want to improve your mobility and wellbeing, osteopathy provides a pathway to better health. To learn more or book an appointment, visit the Principle Four Osteopathy clinic page.
FAQs About Osteopathy
What qualifications do osteopaths have in Australia?
Osteopaths in Australia must complete a university degree (usually a double Bachelor or Master degree), and be registered with AHPRA.
How is osteopathy different from physiotherapy or chiropractic?
While all three professions treat musculoskeletal conditions, osteopathy focuses on holistic, hands-on care, with a strong emphasis on how body systems interrelate.
Do I need a referral to see an osteopath?
No, you can see an osteopath without a referral. However, some chronic care plans under Medicare do require a GP referral.
Is osteopathy covered by private health insurance?
Yes. Most private health insurers offer rebates for osteopathic treatment under extras cover.
Author
Heath Williams (Principal Osteopath, Educator, Workplace Health Consultant)
Heath is the founder of Principle Four Osteopathy and has over 20 years of experience in clinical practice. He combines a strong biomechanical approach with a passion for evidence-based care and patient education. Heath works extensively in occupational health, helping people prevent and recover from workplace-related injuries.