So how many of you know whether your wrists are sitting in the correct place when you are typing or using the mouse? How many of you are not sure whether you should be using a mouse or keyboard wrist support or a different type of keyboard or mouse?
This blog aims to provide you with the ability to assess your current typing wrist position and mouse wrist position and help you identify whether your current working ergonomics are suitable or whether you may require a different keyboard, mouse or use of a wrist support.
Assessing Wrist Position Whilst Using The Mouse
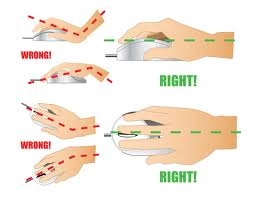
When using the mouse your wrist position should be neutral/straight when looking from the side. As you can see from the top image above. A wrist that is extended or flexed is not desired. Spending a lot of time with your wrist in an extended position (one of the most commonly observed wrist position faults) may increase your wrist of developing wrist and hand strains and sprains.
When using the mouse your wrist should be straight when looking from above. As you can see from the bottom left image above, deviation of the wrist to the left or right is not a desired wrist position. Spending a lot of time using the mouse with ulnar or radial deviation may increase your risk of developing overuse type injuries such as tendinopathies.
For those workers who find that their wrist drops into extension when using it, a wrist support may be of benefit and may help to prevent this wrist extension. For those workers who continue to have issues with their wrist whilst using a mouse, further assessment may be required. Mouse options such as an ortho mouse, vertical mouse and mouse joystick are other options that can be used to improve wrist and mouse ergonomics.
Assessing Wrist Positions Whilst Typing
This image above helps demonstrate what position your wrists should sit in when typing. A quick review of this image above shows the left image to represent an ideal wrist position. The worker in this image above would benefit from the use of a keyboard wrist pad. As the two images represent in the middle and the right, excessive flexion and extension of the wrist are not desired.
Assessing The Mouse Position On The Desk
This image above clearly demonstrates where your mouse and keyboard should sit on the desk. Both should be adjacent to one another and approximately 10cm from the desk edge. A mouse position as demonstrated by the image above on the left results in the mouse arm being outstretched. Often workers who spend a lot of time with their arm in this position may be predisposed to an increased risk of developing neck, shoulder and upper limb strains and sprains.
Note: If you find that you are having ongoing issues with your wrists, forearms, shoulder or neck following adjustments to your workstation, please inform your Human Resources or Occupational Health and Safety Representative to arrange for a further in depth ergonomic risk assessment and guidance. If you are looking for an external consultant (Osteopath, Physiotherapist or Exercise Physiologist) to conduct an assessment, please contact Corporate Work Health Australia. Corporate Work Health Australia www.corporateworkhealth.com are an Australia Wide business providing Ergonomic Risk Assessments in all major cities (Melbourne, Sydney, Brisbane, Adelaide, Hobart, Perth, Canberra and Darwin).
This blog was written by Osteopath Heath Williams. Heath is the director of Principle Four Osteopathy and Corporate Work Health Australia. Principle Four Osteopathy is one of Melbourne City CBD 3000 leading Osteopathic clinics. The clinic is located in the heart of the Melbourne CBD at 29 Somerset Place (near the corner of Little Bourke & Elizabeth St). Appointments can be made by calling 03 9670 9290 or booking online @ www.principlefourosteopathy.com.